

This chapter consists of the items below. If you want to go directly to an item,
1. - Introduction click here!
2. - Convention click here!
3. - Power Analysis in a Circuit click here!
4. - Maximum Power Transfer Theorem click here!
We can define
Another way of expressing the unit of measure of power is to say that if
As
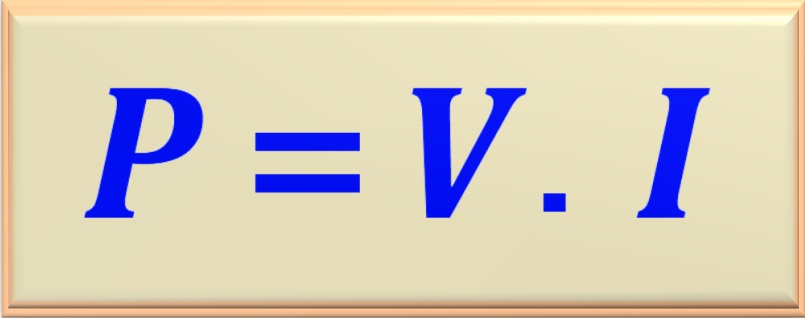
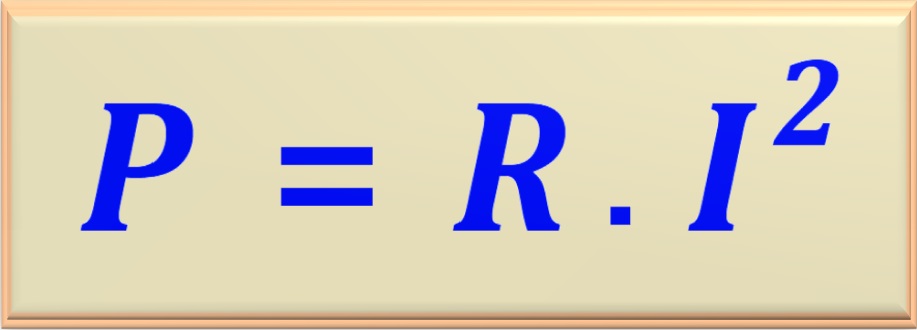
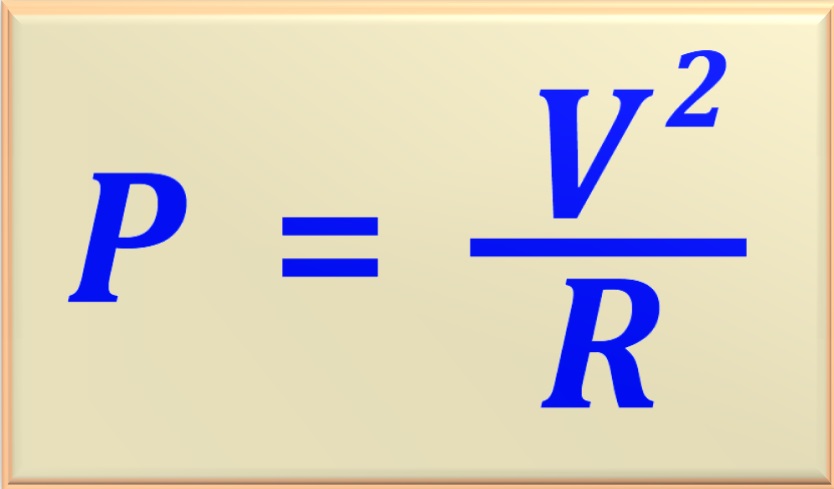
In the study of
Thus, we say that a device is receiving power, if it has signal
So when we read that such a device has, for example,
Notice that in any situation, in an electric circuit, the
In the

To make it clear how we should proceed, we will make a power balance of the circuit.
First, let us calculate the
Summing up algebraically the
One of the designer's concerns is to know under what conditions we can transfer the maximum power to a load
which is connected at the output of a circuit.
To solve this problem we have called the
We can easily prove this theorem by starting from a resistive voltage divider circuit,
where we must consider one of the resistances to be the
Let us anticipate that for this event to happen the following relation must be satisfied:

In other words: whenever the value of
At no point does this theorem
Remember: the
If there are still doubts regarding the above statement, let's take as an example the
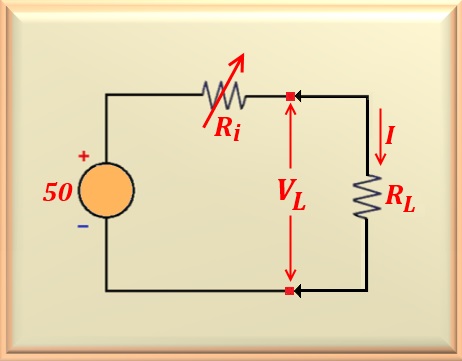
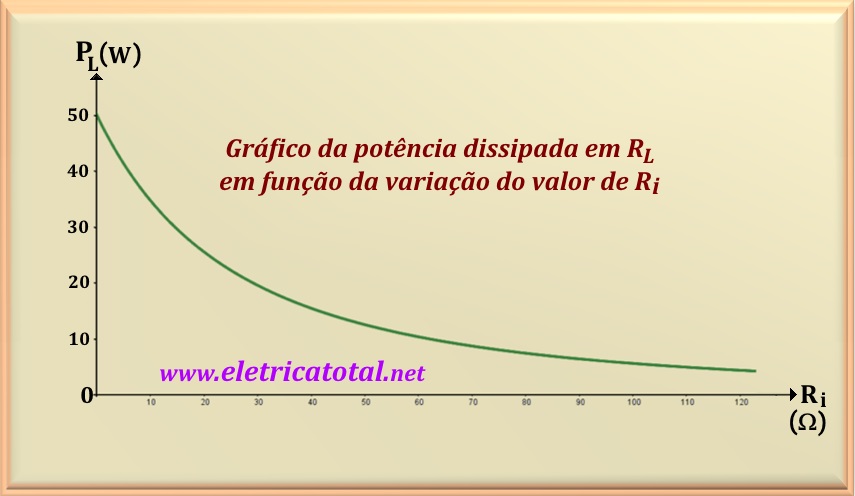
Let us through this example, show how the power dissipated by the load varies
for different values of
Now that we have the electric current flowing through
Doing similarly for the other values of
| Valor de Ri (Ω) | Corrente I (A) | Potência em RL (W) |
| 100 | 0.33 | 5.56 |
| 70 | 0.42 | 8.68 |
| 50 | 0.50 | 12.50 |
| 30 | 0.625 | 19.53 |
| 10 | 0.83 | 34.72 |
| 5 | 0.91 | 41.32 |
| 0 | 1.00 | 50.00 |
In the
In the